Varicose Veins and Degrees And Classification
Varicose veins occurs due to the deterioration of the valves of the vein. The dirty blood which is not transferred properly in the vessels causes structural damage. Extensions formed in veins are called varicose veins.
Varicose veins are diagnosed as 3 groups. These are capillaries, medium and large varices.
In addition, varicose veins are universally rated between 0 and 6 according to the ceap classification. Capillaries, large and medium varices are graded according to ceap classification.
Capillary Vascular Cracking
There are two main groups of vessels in human body, arteries and veins. There are also thin capillaries that connect these main vessels. These capillaries are normally 0.5 mm wide structures. However, it may reach a width of 1.2 mm by the cracking of the veins.
Vascular dilation of the veins cause serious symptoms. However, the expansion of the capillaries does not cause any health complaints. They just cause problems of appearance.
It is usually seen on the face and legs. People concern especially about the ones on the face area because of the esthetic concerns.
Vein dilation causes that the veins become curved and visible from outside of the skin. However, the capillaries do not become palpable from the skin. They just spread like spider webs.
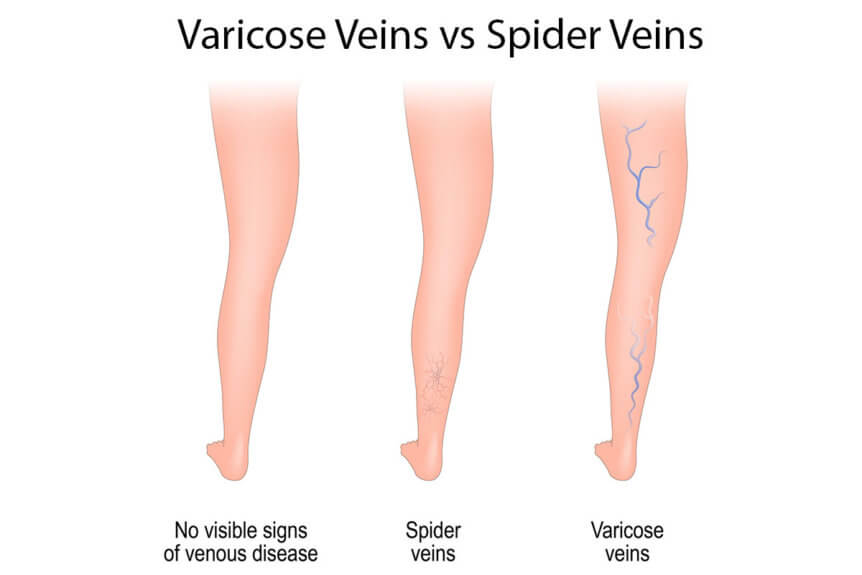
Medium Sized Varicose Veins
They are 2-3 mm enlargements of veins. They are called reticular veins. They have dark green and purple color and curved shapes because they are structurally deteriorated.
In addition to disturbing appearance, they also cause health problems such as cramps.
Medium-sized varices may become large varices over time if left untreated. If the capillaries are not treated, they do not become wider, they only spread.
Large Sized Varicose Veins
Vascular dilatations that are palpable from the skin are larger than 3 mm. Medium-sized varices become large varices when left untreated.
As varicose veins progress, there will be different kinds of new symptoms and increase of the grade of the symptoms. As the problem progresses by time, large varicose veins may cause bleeding complaints. In addition, untreated varicose veins may cause ulcers.
Ceap Classification
Varices are graded between 0 and 6 according to the universally accepted ceap classification.
Ceap-Klassifizierung
Varizen werden gemäß der allgemein akzeptierten Ceap-Klassifikation zwischen 0 und 6 eingestuft.
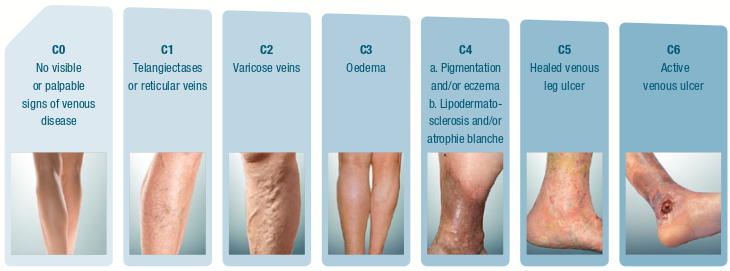
- C0> no symptoms of varicose veins.
- C1> spider web-like capillary varices are detected. Capillaries generally do not cause complaint. However, it may cause slight tingling in some patients.
- C2> variceal onset is detected. Varicose veins at this grade may cause complaints in some patients. Generally, pain and fatigue are seen in the feet due to fatigue and cramps that occur at night.
- C3> swelling and edema symptoms. Untreated reticular veins cause swelling and edema.
- C4> Medium varices are transformed into large varicose veins, with color change and hardening of the legs. This grade is classified as C4. It means that the disease has reached higher grades.
- C5> Untreated mid-size varices progress and become large varices. Bleeding can occur in dilated vessels. While some bleedings are easy to stop, some cases may be seen by a doctor to stop the bleeding.
- C6> The last and most dangerous grade of the disease. At this stage, blood flow in the veins stop completely and leg wounds occur. As there is no blood flow, the wounds do not heal by themselves or they heal difficult even with a treatment. These wounds are called leg ulcers
The sooner varicose veins are treated, the more advantageous for the patient. As treatment is delayed, the varicose veins progress to higher grade varices and becomes larger varices. In the end, leg wounds are difficult to heal and treat. For this reason, varicose veins are recommended to be treated without delay. And it is advised to take precautions to prevent new varicose veins. Otherwise, wounds may occur on the legs as in the shared image.
 IDEA Clinic
IDEA Clinic








